Prostate Surgery
Prostate surgery is commonly performed for two reasons: prostate cancer and benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). Treatment may be life-saving, or it may be done to relieve problems urinating that did not respond to medication.
Your choice of the surgeon may be the most important decision you make, even more so than the type of procedure. The more skilled the surgeon, preferably with extensive experience performing hundreds or even thousands of procedures just like yours, the less likely you are to experience erectile dysfunction due to nerve damage.
In addition to selecting a highly skilled surgeon, it is important to work with your surgeon to select the best procedure for your unique needs. Some procedures are used to shrink prostate tissue, others remove a portion or all of the prostate and may be used to treat cancer.
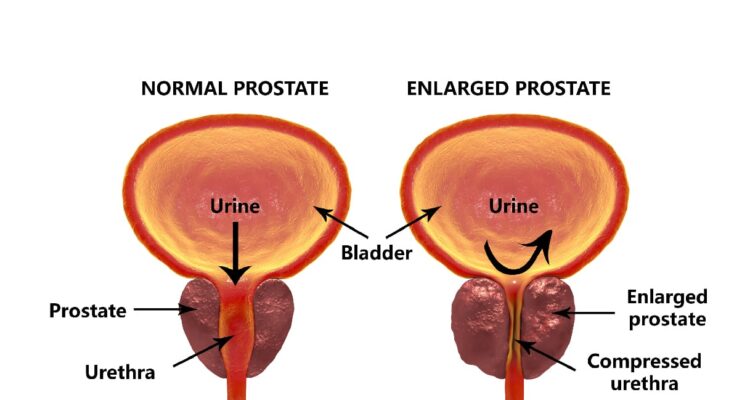
Enlarged Prostate or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
The prostate is a small organ about the size of a walnut. It lies below the bladder (where urine is stored) and surrounds the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder). The prostate makes a fluid that helps to nourish sperm as part of the semen (ejaculatory fluid).
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is nonmalignant (noncancerous) enlargement of the prostate gland, a common occurrence in older men. It is also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Signs and Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia:
The severity of signs and symptoms in people who have Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia or prostate gland enlargement differs, but the effect tends to gradually worsen over time. Common symptoms of prostate gland enlargement include:
- Difficulty in urination
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Weak urine stream. It gradually starts and stops
- Nocturia (increased frequency of urination during nights)
- Unable to completely empty the bladder
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Blood in urine
- Inability to urinate
- Urinary tract infections
- Bladder damage
- Bladder stones
- Kidney damage
Diagnosis of Enlarged Prostate or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia:
- Digital rectal exam: the doctor checks the rectum for determining prostate enlargement
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) blood test
- Urine test: for detecting any kind of infection
- Transrectal ultrasound
- Urodynamic and Pressure Flow Studies: This test measures your bladder pressure and determines how efficiently your bladder muscles are functioning
- Cystoscopy: this procedure is done to examine your bladder and urethra. The doctor will give you a local anesthetic before performing this test
- Prostate biopsy: This is done to check any signs on prostate cancer
Dr Rajesh Dhake has vast experience in diagnosing and successfully treating complex conditions involving Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.
Treatment options:
- Medical Treatment
- Endoscopic Surgery
TURP (monopolar/Bipolar)
Holmium Laser Enucleation of Prostate (HoLEP)
Dr. Rajesh Dhake is one of the Best prostate Cancer doctor in Pune. The doctor is known as who treats prostrate cases giving patients one of the best, fast, smooth recovery and good quality of life for the prostate disease
FAQs
WHAT IS UROLOGY?
Urology is a surgical speciality that addresses male and female diseases of the urinary tract, as well as male reproductive system disorders. Urology is a part of health care that deals with diseases of the male and female urinary tract (kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra). It also deals with the male organs that are able to make babies (penis, testes, scrotum, prostate, etc.). Since health problems in these body parts can happen to everyone, urologic health is important.
WHAT CAN I DO TO MAINTAIN GOOD UROLOGIC HEALTH ?
The best way to avoid urological problems is to maintain good overall health habits, including exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding tobacco, excessive alcohol, and caffeine.You should also avoid foods or substances that remove water from the body, known as diuretics.
THERE’S BLOOD IN MY URINE. WHAT MAY BE THE CAUSE?
The presence of blood in the urine could be the result of a minor cause or a serious underlying medical condition. To determine the source, a urologist will perform a thorough evaluation. The blood could be the result of an infection, kidney or bladder stones, cancer of the urinary system, or injury.
IT’S PAINFUL TO URINATE. WHAT COULD BE CAUSING THE PROBLEM?
There are many conditions that could result in painful urination. An infection of the urinary tract or prostate is a common cause, along with obstructions in the urethra, kidney, bladder, or prostate.