Vesicovaginal Fistula
Vesicovaginal fistula (VVF) is a subtype of female urogenital fistula (UGF). VVF is an abnormal fistulous tract extending between the bladder and the vagina that allows the continuous involuntary discharge of urine into the vaginal vault. In addition to the medical sequelae from these fistulas, they often have a profound effect on the patient’s emotional well-being. A vesicovaginal fistula is an unwanted opening that forms between the bladder and the wall of the vagina. The causes for this can include infections, injuries, and inflammation.
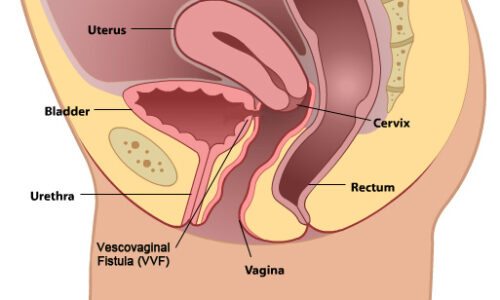
What is a vesicovaginal fistula?
A fistula is an unwanted opening that develops between two parts of the body. The causes for this can include infections, injuries, and inflammation. Fistulas can occur in many parts of the body.
A vesicovaginal fistula is an opening that develops between the bladder and the wall of the vagina. The result is that urine leaks out of the vagina, sometimes lightly but it can be steady if the fistula is large. In addition to being a serious medical problem, this condition is very upsetting to women. The leakage is embarrassing and can smell bad.
Causes
Vesicovaginal fistulas are often a complication after surgery to treat problems in the bladder or vagina. They also can be linked to gynaecological cancer, either from the disease or sometimes as a side effect of radiation therapy or surgery to treat cancer. Particularly bad or repeat urinary tract infections can sometimes lead to fistulas too, but this is rare.
- Abdominal surgery
- Pelvic, cervical, or colon cancer
- Radiation treatment
- Bowel disease like Crohn’s or diverticulitis
- Infection (including after an episiotomy or a tear you had when you gave birth)
- Traumatic injury, such as from a car accident
Management options:
- Lap /open transabdominal VVF repair
- Vaginal VVF repair
- VVF fulguration
FAQs
WHAT IS UROLOGY?
Urology is a surgical speciality that addresses male and female diseases of the urinary tract, as well as male reproductive system disorders. Urology is a part of health care that deals with diseases of the male and female urinary tract (kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra). It also deals with the male organs that are able to make babies (penis, testes, scrotum, prostate, etc.). Since health problems in these body parts can happen to everyone, urologic health is important.
WHAT CAN I DO TO MAINTAIN GOOD UROLOGIC HEALTH ?
The best way to avoid urological problems is to maintain good overall health habits, including exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding tobacco, excessive alcohol, and caffeine.You should also avoid foods or substances that remove water from the body, known as diuretics.
THERE’S BLOOD IN MY URINE. WHAT MAY BE THE CAUSE?
The presence of blood in the urine could be the result of a minor cause or a serious underlying medical condition. To determine the source, a urologist will perform a thorough evaluation. The blood could be the result of an infection, kidney or bladder stones, cancer of the urinary system, or injury.
IT’S PAINFUL TO URINATE. WHAT COULD BE CAUSING THE PROBLEM?
There are many conditions that could result in painful urination. An infection of the urinary tract or prostate is a common cause, along with obstructions in the urethra, kidney, bladder, or prostate.